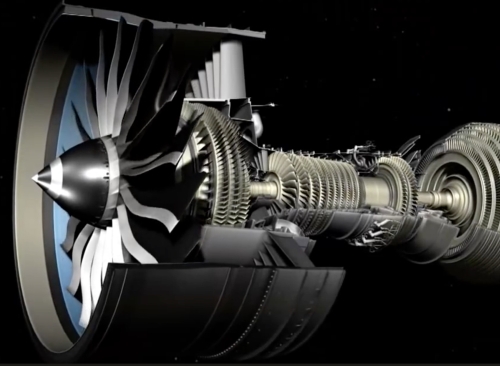
Advanced Manufacturing technologies have become one of the most important parts of the Aerospace industry. This is because of the unique challenges that the aircraft designers deal with. The aircraft designs need to consider the environmental conditions using strong materials that are both lightweight and temperature resistant. Such designs require micro and Nano- machining techniques. Here are four advanced machining technologies that are used in the Aerospace industry.
Additive Manufacturing
The Aerospace industry was quick to identify the benefits and potential of Additive Manufacturing to design its planes. The technology uses Power-Bed laser printing systems to build its most components. Additive manufacturing technology is used to build structures that work within the fuselage with features such as reduced weight and reduce heat. An additive manufacturing technique, commonly known as the Fused Deposition Modeling, is used to create semi-hollow parts of the aircraft wings by both adding strength and reducing weight.
Composite Materials
Composite materials are widely used to design aircraft. Aerospace engineers prefer using these materials because of their favorable characteristics of flexibility, strength, temperature and chemical resistance. Composite materials and advanced polymers in the design help to improve performance and reduce lifecycle costs. These materials also reduce the overall weight of the aircraft cutting short their fuel consumption and carbon emissions.
Robotics
Robots are used in the aerospace industry to manage the labor-intensive process, particularly when lifting and handling tasks are to be done. The industry is using powerful robots in its manufacturing plants to move and join aircraft parts. Robotics is also taking care of manufacturing process that is hazardous to people such as painting and welding.
Laser Beam Welding
This technology offers rapid and high precision work as compared to the traditional welding techniques. Laser welding is, therefore, a preferred solution for handling materials when repeatability and high accuracy is required. The most advantageous property of this technique is that it transfers very little heat to the material that is welded. This way it does not create a heat affected zone around the weld, ultimately not compromising the strength and performance of the material.
With the widespread use of these technologies, the aerospace industry has also inspired several other industries to use these technologies in the manufacturing process. These techniques have undoubtedly simplified the manufacturing processes and reduced costs to a greater extent. Their accuracy and precision have reduced the number of failure points in the manufacturing process.