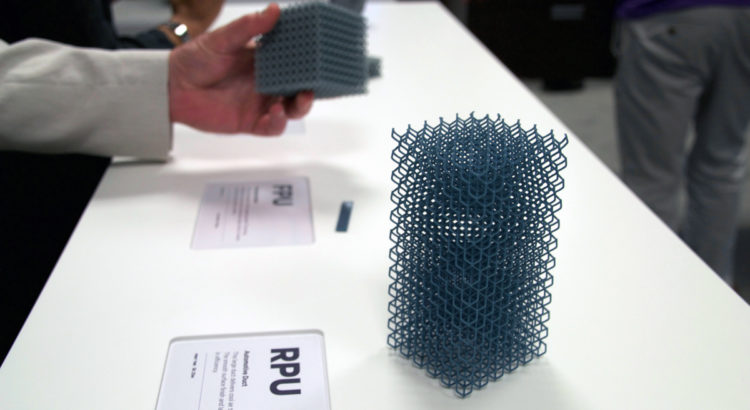
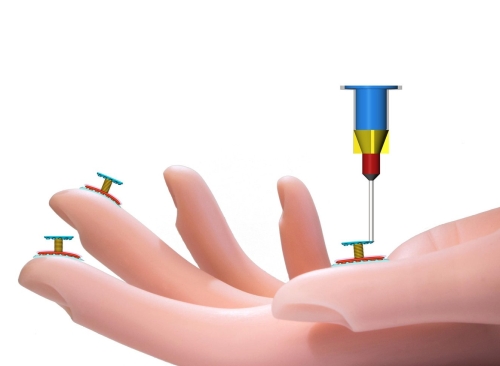
If you have bought a 3D printer, and have printed some of the stuff, then you must know what plastic material you need to work with. Different plastic materials have different characteristics and are utilized for certain products. Hence, it is important to know what kinds of plastics are used in 3D printing.
Types of materials used in 3D printing
Naturally occurring organic plastics have been utilized by humans for thousands of years. The use of synthetic plastics was started in mid of 19th century. Gradually by the mid of 20th century, developments in chemical technologies lead to a new era of plastic materials. Plastics are widely used as 3D printing materials. Here, are some types of materials which lead to the origination of 3D printing plastic:
Photopolymers

These polymers are liquid plastic resin that changes into solid form when exposed to light. This UV-curable resin is made up of three main components: Binders, Monomers and, Photoinitiators which are mostly mixed with additives, chemical agents, colorants and plasticizers.
Thermoplastics
They are not as complex as photopolymers. These plastic polymers become moldable at a certain temperature and harden upon cooling. They can also be remelted as per the requirements. Thermoplastics are used in selective laser sintering and fused deposition modelling.
Bioplastics

Substituting conventional plastics with bio-based plastics, made from renewable feedstocks, is an excellent way to mitigate the harmful impact of plastics on the environment. Polylactic Acid (PLA), which is a thermoplastics polymer derived from renewable sources and is the most preferred choice of plastic for 3D printing.
Upcoming 3D printing plastic
There are many organizations which are creating 3D printing plastic from renewable sources and are taking measures to keep the environment clean and protected. Many organizations are also focussed on manufacturing machinery for recycling plastic objects to make 3D printing filaments. All in all, 3D printing the future of the digital world, and it is vital to know about the raw materials used in it to ensure that it is environment-friendly.